# Ejemplos de Diagramas como Código
Este repositorio contiene ejemplos de diagramas de arquitectura generados mediante código utilizando la biblioteca `diagrams` en Python. Esta herramienta permite crear representaciones visuales de arquitecturas de software de manera programática.
## Instalación
Crear un entorno virtual y activarlo:
```bash
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
```
Instalar la biblioteca `diagrams`, puedes utilizar `pip`:
```bash
pip install diagrams
```
Al terminal se puede desactivar el entorno virtual con el comando:
```bash
deactivate
```
## Ejemplos
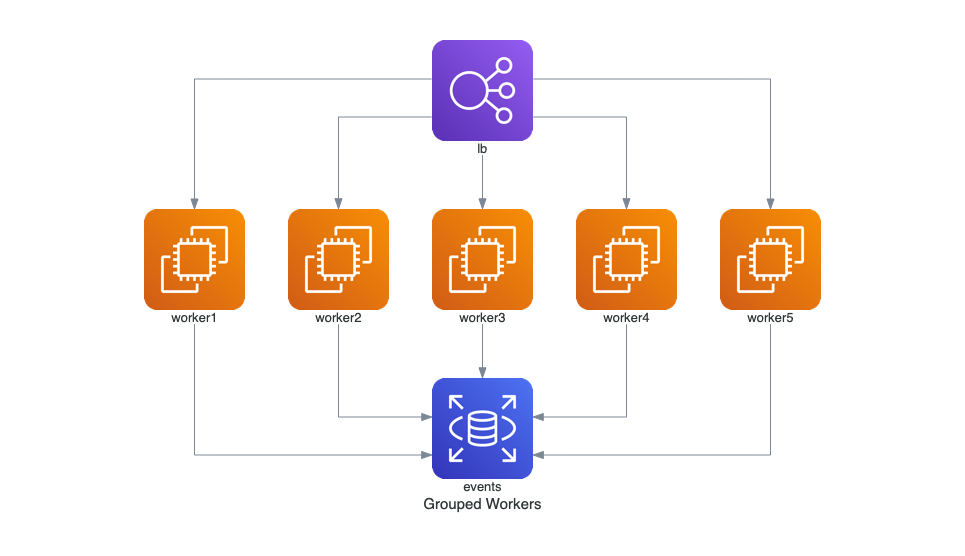
### Trabajadores Agrupados en AWS
Este diagrama muestra un balanceador de carga (ELB) distribuyendo el tráfico a múltiples instancias de EC2, las cuales interactúan con una base de datos RDS.
```python
from diagrams import Diagram
from diagrams.aws.compute import EC2
from diagrams.aws.database import RDS
from diagrams.aws.network import ELB
with Diagram("Grouped Workers", show=False, direction="TB"):
ELB("lb") >> [EC2("worker1"),
EC2("worker2"),
EC2("worker3"),
EC2("worker4"),
EC2("worker5")] >> RDS("events")
```
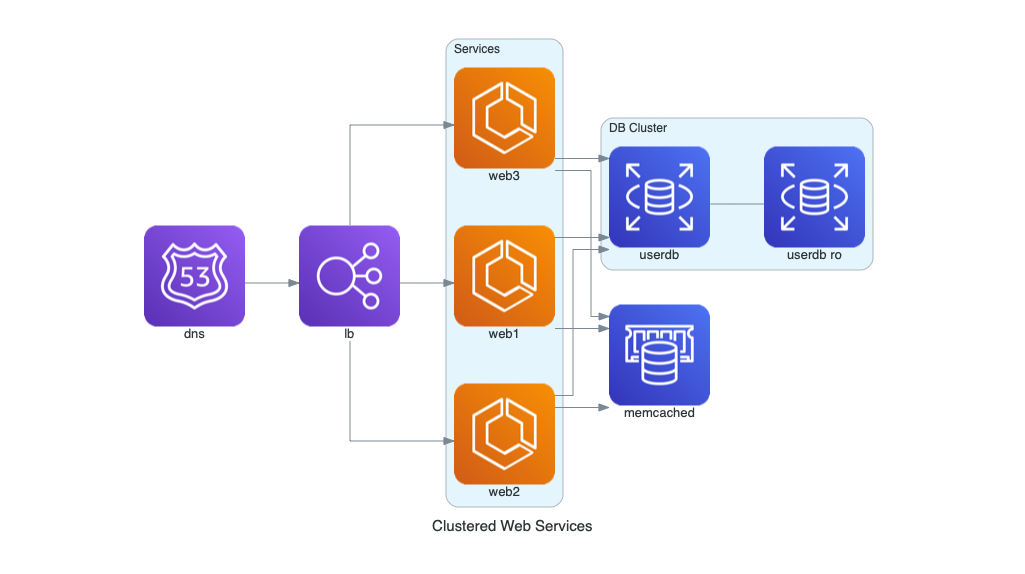
### Servicios Web en Clúster
Este diagrama ilustra una arquitectura de servicios web en AWS. Incluye balanceo de carga, clúster de servicios, almacenamiento en caché y una base de datos principal con réplica.
```python
from diagrams import Cluster, Diagram
from diagrams.aws.compute import ECS
from diagrams.aws.database import ElastiCache, RDS
from diagrams.aws.network import ELB
from diagrams.aws.network import Route53
with Diagram("Clustered Web Services", show=False):
dns = Route53("dns")
lb = ELB("lb")
with Cluster("Services"):
svc_group = [ECS("web1"),
ECS("web2"),
ECS("web3")]
with Cluster("DB Cluster"):
db_primary = RDS("userdb")
db_primary - [RDS("userdb ro")]
memcached = ElastiCache("memcached")
dns >> lb >> svc_group
svc_group >> db_primary
svc_group >> memcached
```
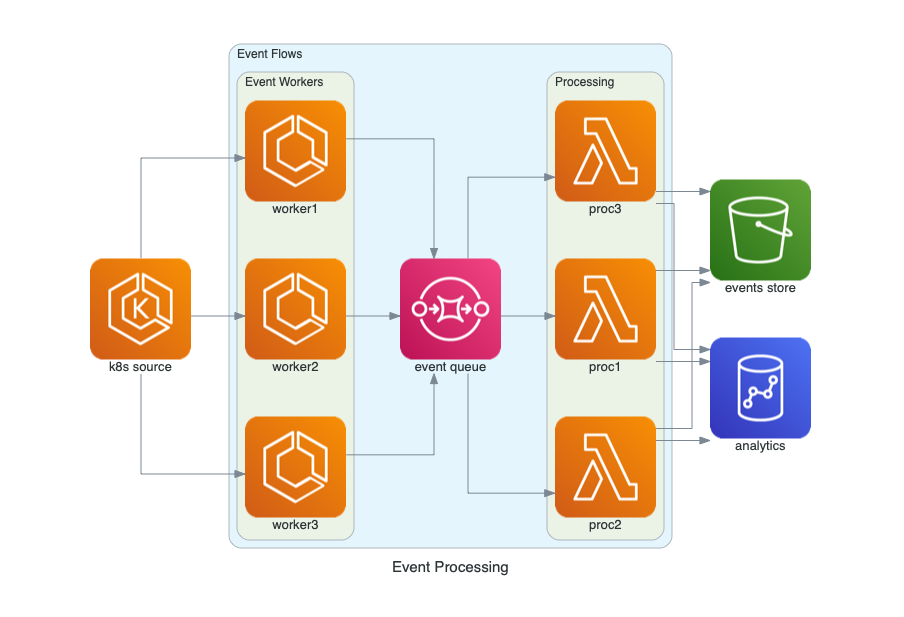
### Procesamiento de Eventos en AWS
El siguiente diagrama representa un flujo de procesamiento de eventos en AWS, utilizando fuentes de eventos, colas para manejar los eventos, procesamiento mediante Lambdas, y almacenamiento en Redshift y S3.
```python
from diagrams import Cluster, Diagram
from diagrams.aws.compute import ECS, EKS, Lambda
from diagrams.aws.database import Redshift
from diagrams.aws.integration import SQS
from diagrams.aws.storage import S3
with Diagram("Event Processing", show=False):
source = EKS("k8s source")
with Cluster("Event Flows"):
with Cluster("Event Workers"):
workers = [ECS("worker1"),
ECS("worker2"),
ECS("worker3")]
queue = SQS("event queue")
with Cluster("Processing"):
handlers = [Lambda("proc1"),
Lambda("proc2"),
Lambda("proc3")]
store = S3("events store")
dw = Redshift("analytics")
source >> workers >> queue >> handlers
handlers >> store
handlers >> dw
```
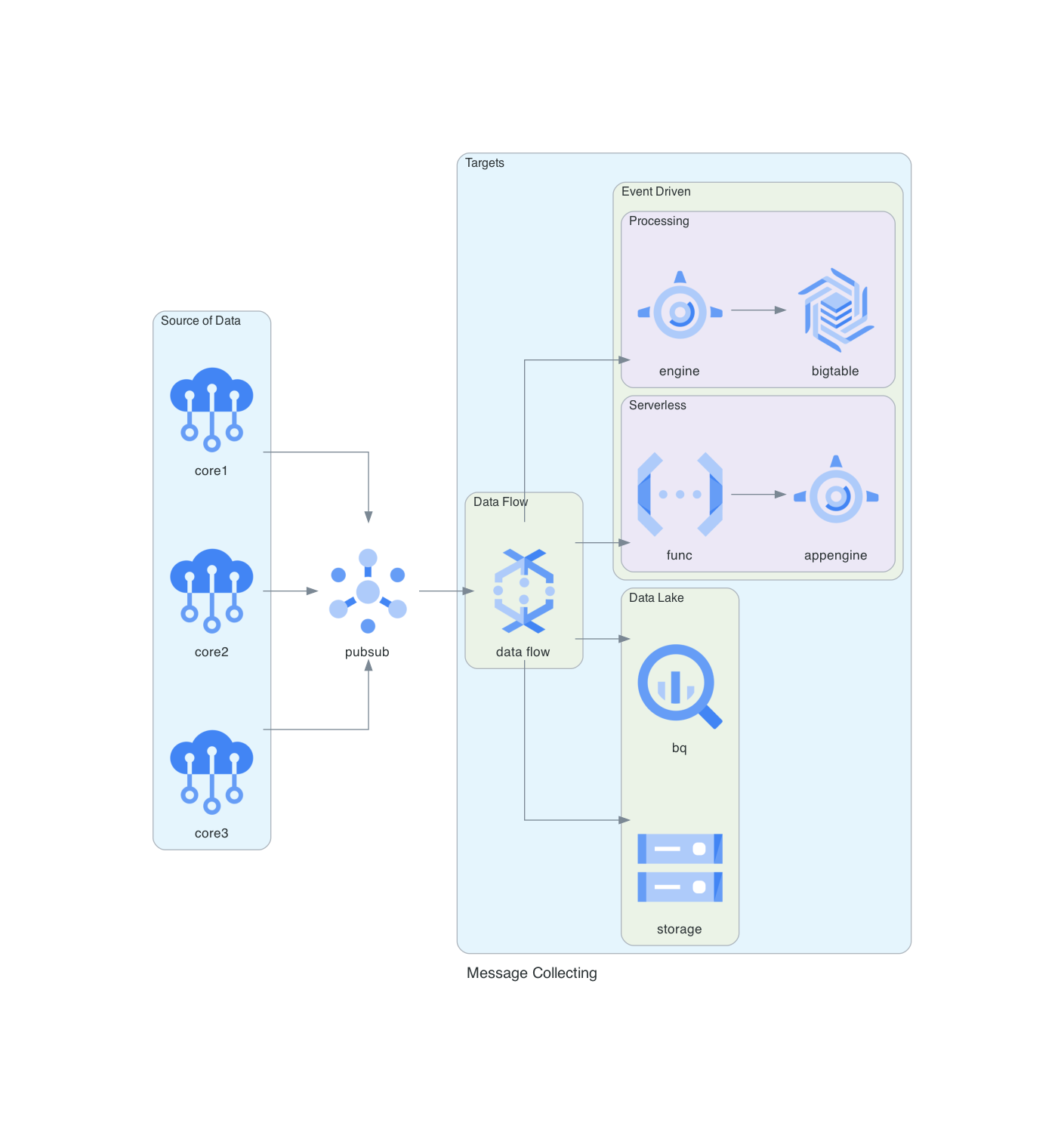
### Sistema de Recolección de Mensajes en GCP
Este diagrama detalla un sistema de recolección de mensajes implementado en Google Cloud Platform (GCP), destacando el uso de Pub/Sub, BigQuery, Dataflow y otras herramientas de GCP.
```python
from diagrams import Cluster, Diagram
from diagrams.gcp.analytics import BigQuery, Dataflow, PubSub
from diagrams.gcp.compute import AppEngine, Functions
from diagrams.gcp.database import BigTable
from diagrams.gcp.iot import IotCore
from diagrams.gcp.storage import GCS
with Diagram("Message Collecting", show=False):
pubsub = PubSub("pubsub")
with Cluster("Source of Data"):
[IotCore("core1"),
IotCore("core2"),
IotCore("core3")] >> pubsub
with Cluster("Targets"):
with Cluster("Data Flow"):
flow = Dataflow("data flow")
with Cluster("Data Lake"):
flow >> [BigQuery("bq"),
GCS("storage")]
with Cluster("Event Driven"):
with Cluster("Processing"):
flow >> AppEngine("engine") >> BigTable("bigtable")
with Cluster("Serverless"):
flow >> Functions("func") >> AppEngine("appengine")
pubsub >> flow
```
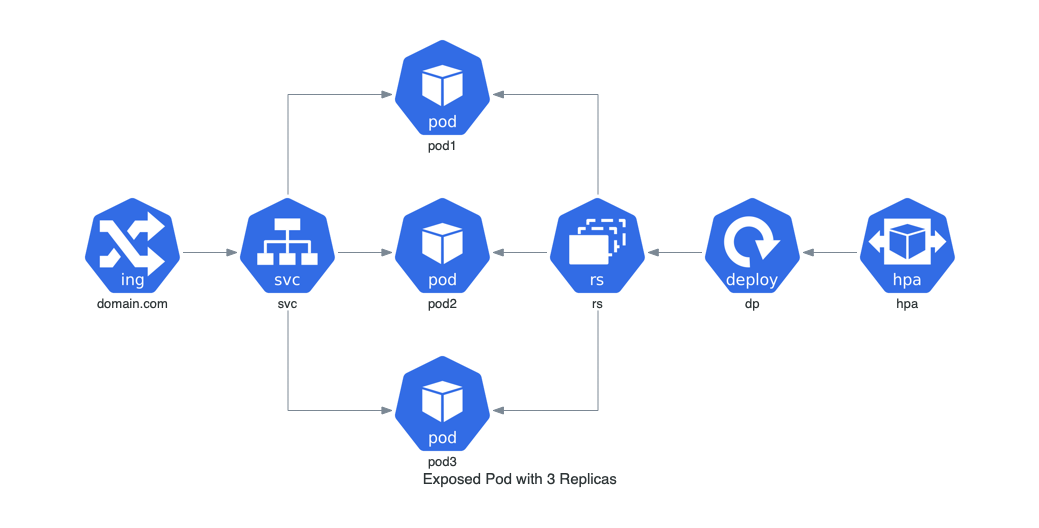
### Pod Expuesto con 3 Réplicas en Kubernetes
Este ejemplo muestra un pod expuesto con un servicio de red en Kubernetes, ilustrando el uso de pods y réplicas.
```python
from diagrams import Diagram
from diagrams.k8s.clusterconfig import HPA
from diagrams.k8s.compute import Deployment, Pod, ReplicaSet
from diagrams.k8s.network import Ingress, Service
with Diagram("Exposed Pod with 3 Replicas", show=False):
net = Ingress("domain.com") >> Service("svc")
net >> [Pod("pod1"),
Pod("pod2"),
Pod("pod3")] << ReplicaSet("rs") << Deployment("dp") << HPA("hpa")
```
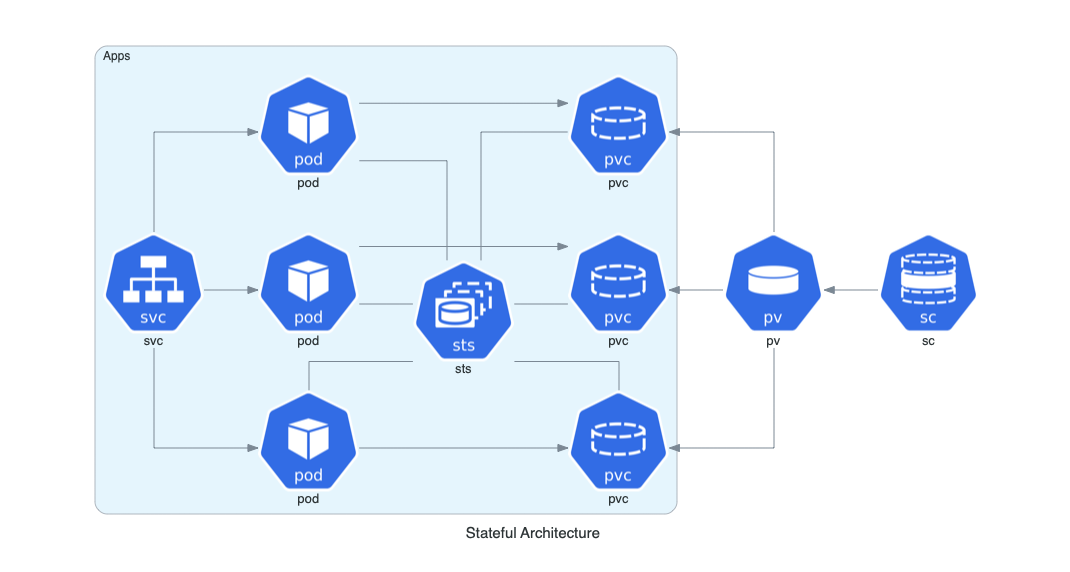
### Arquitectura con Estado en Kubernetes
Esta arquitectura representa un conjunto de aplicaciones stateful en Kubernetes, mostrando el uso de StatefulSets, almacenamiento persistente y clases de almacenamiento.
```python
from diagrams import Cluster, Diagram
from diagrams.k8s.compute import Pod, StatefulSet
from diagrams.k8s.network import Service
from diagrams.k8s.storage import PV, PVC, StorageClass
with Diagram("Stateful Architecture", show=False):
with Cluster("Apps"):
svc = Service("svc")
sts = StatefulSet("sts")
apps = []
for _ in range(3):
pod = Pod("pod")
pvc = PVC("pvc")
pod - sts - pvc
apps.append(svc >> pod >> pvc)
apps << PV("pv") << StorageClass("sc")
```
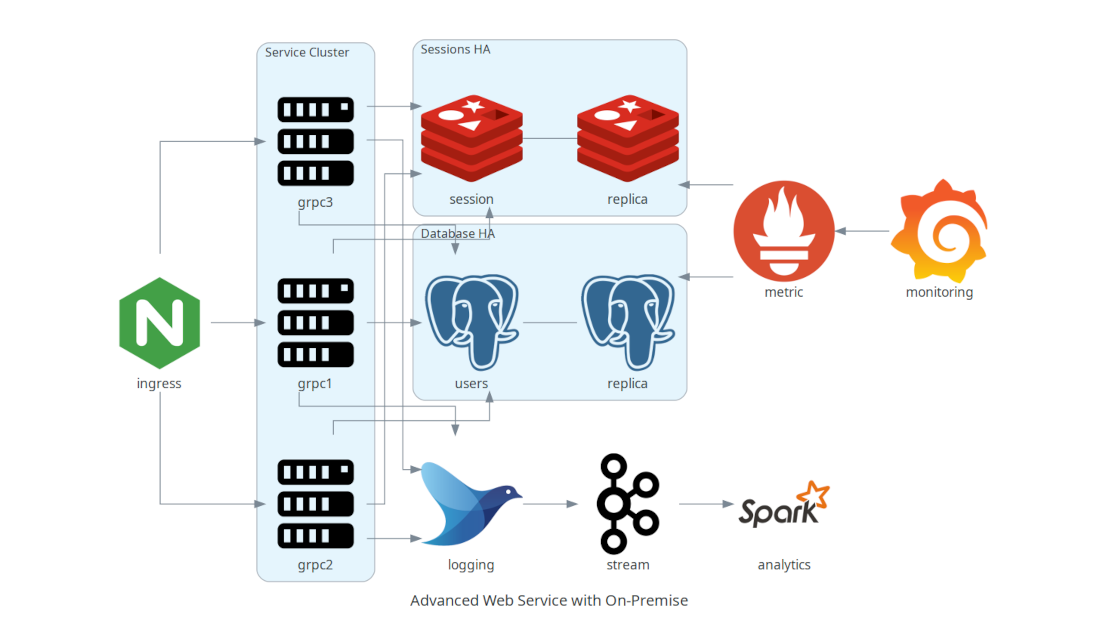
### Servicio Web Avanzado con Infraestructura On-Premise
Aquí se ilustra un servicio web avanzado que combina infraestructura local (on-premise) con herramientas como Nginx, Redis, PostgreSQL y Kafka para el manejo de servicios, sesiones y base de datos.
```python
from diagrams import Cluster, Diagram
from diagrams.onprem.analytics import Spark
from diagrams.onprem.compute import Server
from diagrams.onprem.database import PostgreSQL
from diagrams.onprem.inmemory import Redis
from diagrams.onprem.aggregator import Fluentd
from diagrams.onprem.monitoring import Grafana, Prometheus
from diagrams.onprem.network import Nginx
from diagrams.onprem.queue import Kafka
with Diagram("Advanced Web Service with On-Premise", show=False):
ingress = Nginx("ingress")
metrics = Prometheus("metric")
metrics << Grafana("monitoring")
with Cluster("Service Cluster"):
grpcsvc = [
Server("grpc1"),
Server("grpc2"),
Server("grpc3")]
with Cluster("Sessions HA"):
primary = Redis("session")
primary - Redis("replica") << metrics
grpcsvc >> primary
with Cluster("Database HA"):
primary = PostgreSQL("users")
primary - PostgreSQL("replica") << metrics
grpcsvc >> primary
aggregator = Fluentd("logging")
aggregator >> Kafka("stream") >> Spark("analytics")
ingress >> grpcsvc >> aggregator
```
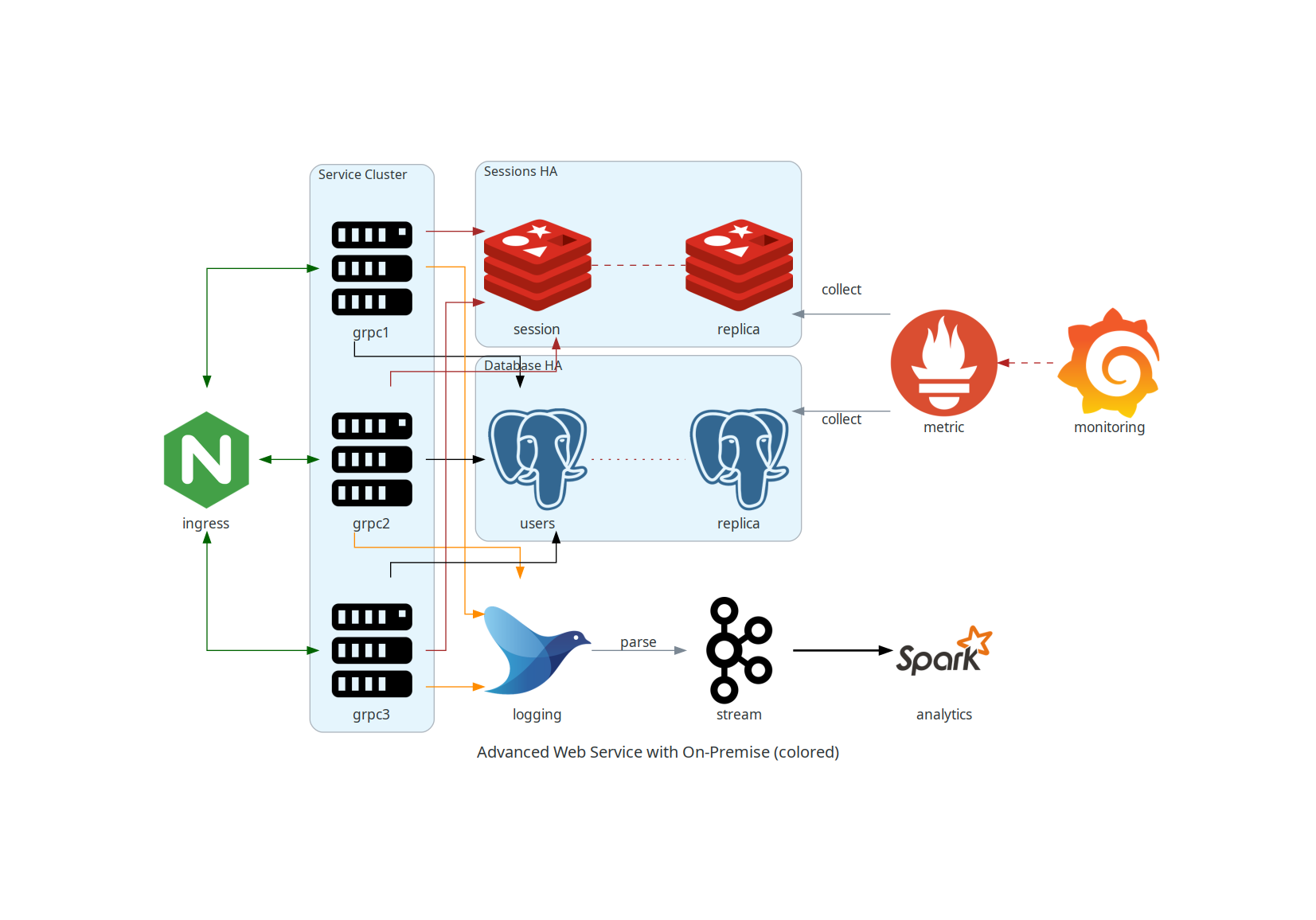
### Servicio Web Avanzado con Infraestructura On-Premise (con colores y etiquetas)
Este diagrama es una versión coloreada del anterior, incluyendo etiquetas y estilos para una mejor comprensión visual.
```python
from diagrams import Cluster, Diagram, Edge
from diagrams.onprem.analytics import Spark
from diagrams.onprem.compute import Server
from diagrams.onprem.database import PostgreSQL
from diagrams.onprem.inmemory import Redis
from diagrams.onprem.aggregator import Fluentd
from diagrams.onprem.monitoring import Grafana, Prometheus
from diagrams.onprem.network import Nginx
from diagrams.onprem.queue import Kafka
with Diagram(name="Advanced Web Service with On-Premise (colored)", show=False):
ingress = Nginx("ingress")
metrics = Prometheus("metric")
metrics << Edge(color="firebrick", style="dashed") << Grafana("monitoring")
with Cluster("Service Cluster"):
grpcsvc = [
Server("grpc1"),
Server("grpc2"),
Server("grpc3")]
with Cluster("Sessions HA"):
primary = Redis("session")
primary - Edge(color="brown", style="dashed") - Redis("replica") << Edge(label="collect") << metrics
grpcsvc >> Edge(color="brown") >> primary
with Cluster("Database HA"):
primary = PostgreSQL
("users")
primary - Edge(color="brown", style="dotted") - PostgreSQL("replica") << Edge(label="collect") << metrics
grpcsvc >> Edge(color="black") >> primary
aggregator = Fluentd("logging")
aggregator >> Edge(label="parse") >> Kafka("stream") >> Edge(color="black", style="bold") >> Spark("analytics")
ingress >> Edge(color="darkgreen") << grpcsvc >> Edge(color="darkorange") >> aggregator
```
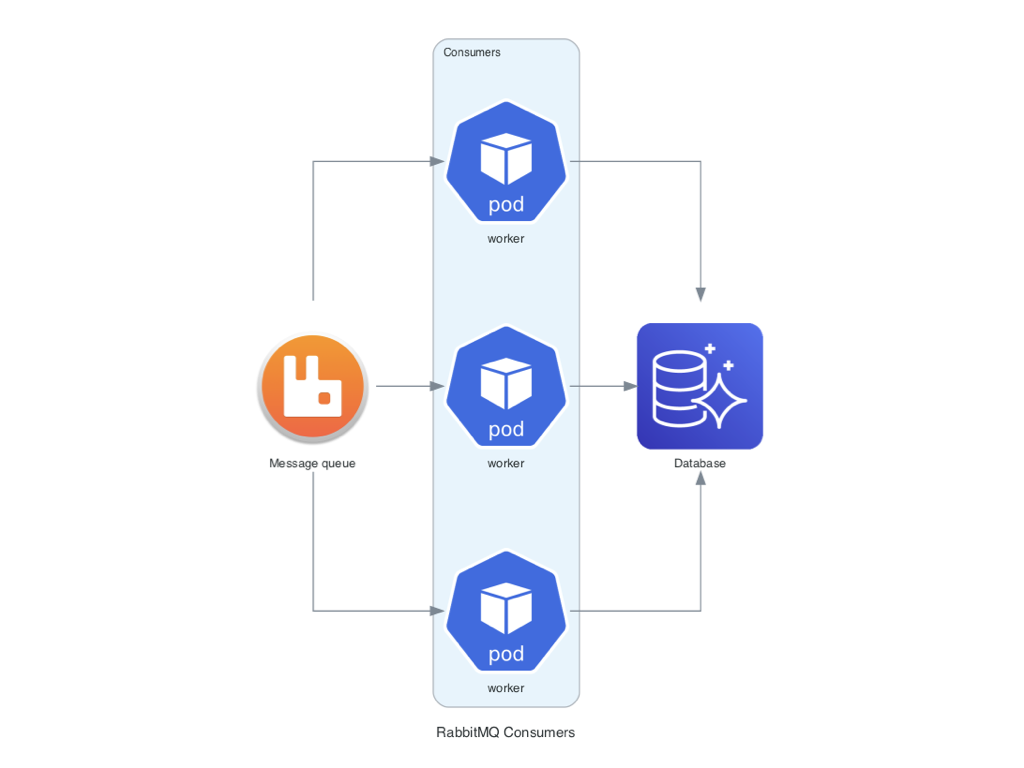
### Consumidores RabbitMQ con Nodos Personalizados
Este ejemplo demuestra cómo incluir nodos personalizados en los diagramas, usando RabbitMQ y Aurora como base de datos de destino.
```python
from urllib.request import urlretrieve
from diagrams import Cluster, Diagram
from diagrams.aws.database import Aurora
from diagrams.custom import Custom
from diagrams.k8s.compute import Pod
# Descargar una imagen para usarla en un nodo personalizado
rabbitmq_url = "https://jpadilla.github.io/rabbitmqapp/assets/img/icon.png"
rabbitmq_icon = "rabbitmq.png"
urlretrieve(rabbitmq_url, rabbitmq_icon)
with Diagram("Broker Consumers", show=False):
with Cluster("Consumers"):
consumers = [
Pod("worker"),
Pod("worker"),
Pod("worker")]
queue = Custom("Message queue", rabbitmq_icon)
queue >> consumers >> Aurora("Database")
```
---
Cada diagrama fue generado utilizando la librería `diagrams`, que permite crear representaciones visuales de infraestructuras y arquitecturas tecnológicas de manera programática. Para más información, visita la [documentación oficial de diagrams](https://diagrams.mingrammer.com/).









